
![]()
Appendectomy Using the Linear Dissecting Stapler
End Sigmoid Colostomy With Hartmann's Pouch
Anterior Resection of the Colon With Low Anastomosis Using the Gambee Suture Technique
Low Anastomosis of Colon to Rectum Using the End-to-End Surgical Stapler Technique
Anterior Resection of the Colon With Low Anastomosis via the Strasbourg-Baker Technique
Appendectomy
Incidental appendectomy can be performed in association with other pelvic surgical procedures. It must be performed when there is clinical evidence of acute appendicitis.
The purpose of the operation is to remove the appendix prior to rupture in cases of acute appendicitis or remove it because it is involved in other pelvic pathology such as endometriosis.
Pathophysiologic Changes: Although the appendix may be associated with the immune response, its exact function remains unclear. Generally no obvious clinical pathophysiologic effect can be found after its removal.
Points of Caution: Hemostasis and aseptic removal of the appendix are keys to the success of this operation. Although the appendiceal stump has traditionally been inverted, there are excellent series showing no apparent sequelae from failure to invert the stump.
Technique
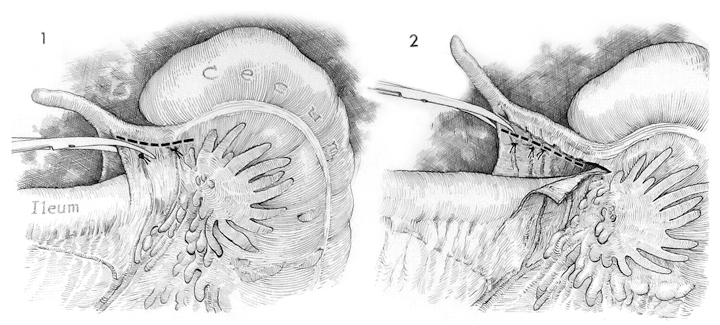
A laparotomy is performed through a McBurney or a lower midline incision. If the diagnosis is uncertain and pelvic inflammatory disease is a possibility, the incision should be lower midline. Identification of the cecum facilitates location of the appendix. The appendix should be placed on traction. Adhesions in the area of the appendix are lysed with Metzenbaum scissors.
The mesoappendix is identified and small Halsted hemostat clamps are used to open avascular sections in the mesoappendix between blood vessels. The tissue between these openings is clamped and tied with 3/0 synthetic absorbable suture. The mesoappendix is incised above the ties.
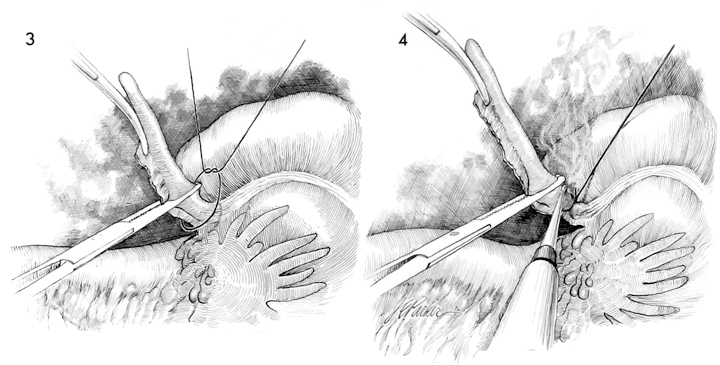
The appendix is elevated. A 0 synthetic absorbable suture is tied around the base of the appendix. A hemostat is placed across the appendix approximately 1 cm from the suture.
The appendix is transected with the electrocautery above the suture.
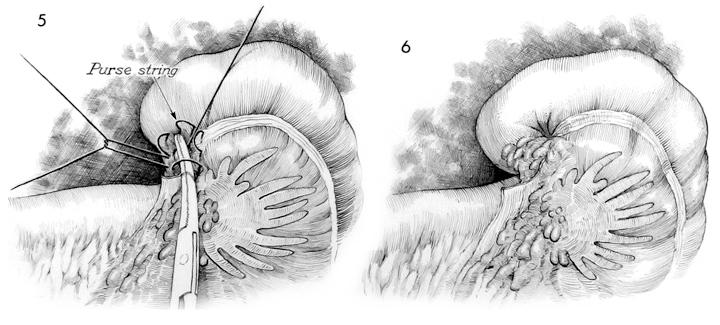
A purse string suture of 3/0 synthetic absorbable suture is placed around the appendiceal stump and a Kelly clamp is used to invert the stump of the appendix as the purse string suture is tied.
The completed operation shows an inverted appendiceal stump. Care should be taken to inspect the vascular ligatures on the mesoappendix blood vessels.
The area should be irrigated with normal saline solution prior to closure of the abdominal wall. No drain is used unless the appendix has ruptured prior to appendectomy.