|
||||||
Small
Bowel Resection Small
Bowel Bypass Small
Bowel Bypass Terminal
Ileectomy |
Small
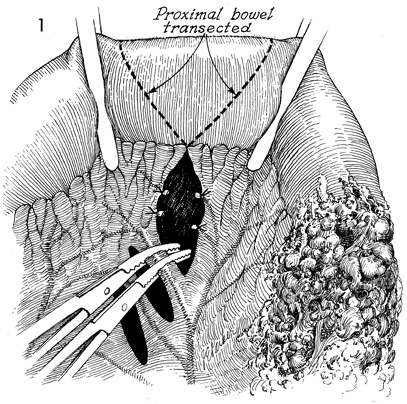
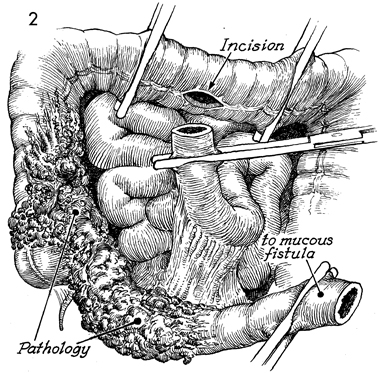
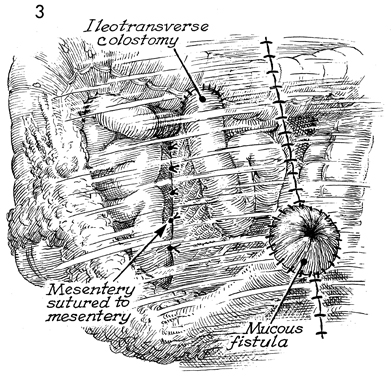
Bowel Bypass With Ileotransverse colostomy with mucous fistula is utilized when the disease process involves the major portion of the terminal ileum plus the ascending colon. The transverse colon may be the ideal site for a small bowel bypass, since it has had little if any ionizing irradiation. Anastomosis at this site reduces the length of colon available for the absorption of intestinal contents, however, and the patient must adapt to living with a more liquid fecal stream than if additional colon were usable. The technique for performing the operation is similar to the other small bowel bypasses with end-to-end anastomosis of the ileum into the colon. The purpose of the operation is to reestablish intestinal continuity and bypass the diseased segment of small intestine. Physiologic Changes. Once the anastomoses are begun between the small bowel and the transverse colon, the length of colon available for absorption of intestinal contents is reduced. This is particularly true if the disease process is such that a diverting cutaneous colostomy is needed. The patient can "run out" of colon. Care must be taken to ensure that at least 20-25 cm of colon are available for anastomosis. There will be a marked difference in the quality of life for the patient if sufficient colon is available to absorb fluid from the fecal stream and produce a firm stool rather than a continuous flow of liquid. Points of Caution. The points of caution are the same as for other small bowel bypasses. Care must be taken to avoid spillage of raw stool into the peritoneal cavity. Preoperative antibiotics should be used. The peritoneal cavity should be thoroughly lavaged after the procedure. A closed suction drain should be placed adjacent to the anastomosis. Technique The technique for ileotransverse colostomy with mucous fistula is similar to that for the ileoascending colostomy with mucous fistula.
|
|||||
Copyright - all rights reserved / Clifford R. Wheeless,
Jr., M.D. and Marcella L. Roenneburg, M.D.
All contents of this web site are copywrite protected.