|
||||||
Diagnostic
Uses Demonstration Laparoscopic
Resection Ovarian
Biopsy Electrocoagulation
of Lysis
or Adhesions Control
of Hemorrhage Sterilization
by Silastic
Band Sterilization Hulka
Clip Sterilization Sterilization
by the Sterilization
by the Sterilization
by the Sterilization - Ucheda Technique Tuboplasty
- |
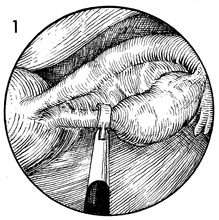
Ovarian Biopsy via Laparoscopy Biopsy of the ovary is rarely necessary. Modern cytogenetic and endocrine
laboratory techniques can usually ascertain whether the ovary contains
oocytes. There are some cases, however, in which biopsy of the ovary
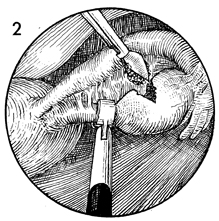
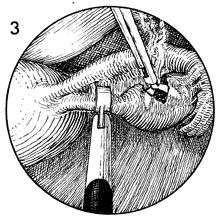
may be indicated. The purpose of the operation is to obtain an adequate biopsy of the ovary through the laparoscope. Physiologic Changes. Removal of a piece of ovary can, in some cases, change the physiology of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis in the same manner as wedge resection of the ovary alters the physiology in polycystic ovary disease. Points of Caution. The predominant complication from ovarian biopsy is control of hemorrhage from the bed of the ovary. Thorough electrocoagulation of the entire biopsy site should be performed. The site should be observed for at least 3-4 minutes to ensure that hemostasis is complete. Technique
|
|||||
Copyright - all rights reserved / Clifford R. Wheeless,
Jr., M.D. and Marcella L. Roenneburg, M.D.
All contents of this web site are copywrite protected.