|
||||
Directed Biopsy of the Cervix at Colposcopy Endocervical
Curettage Conization
of the Abdominal
Excision Correction
of an Incompetent Cervix Correction
of an Incompetent Cervix |
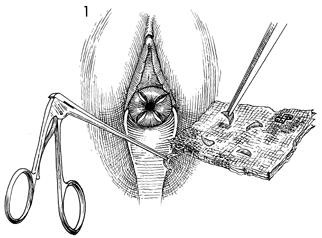
Biopsy of the Cervix Randomized biopsy of the cervix is indicated whenever a gross lesion of the cervix is seen. All too often, gross lesions are diagnosed on sight as cervical "erosions or eversions" without histologic confirmation. The Papanicolaou smear alone is not sufficient for diagnosing gross lesions of the cervix. The purpose of the operation is to obtain a histologic specimen of the squamocolumnar junction of the cervix. Physiologic Changes. None. Points of Caution. Cervical carcinoma begins at the squamocolumnar junction. Therefore, it is essential that this junction to be taken in any biopsy of the cervix. This operation has been illustrated in conjunction with Dilatation and Curettage. Technique
|
|||
Copyright - all rights reserved / Clifford R. Wheeless,
Jr., M.D. and Marcella L. Roenneburg, M.D.
All contents of this web site are copywrite protected.