|
||||||
Bartholin's Gland Cyst Marsupialization Excision of Vulvar Skin, with Split-Thickness Skin Graft Vaginal
Outlet Closure of Wide Local Excision of the Vulva Wide
Local Excision Alcohol
Injection Cortisone
Injection Excision
of the |
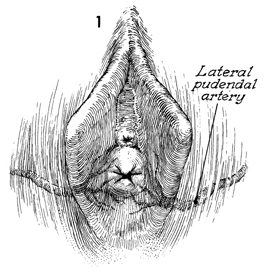
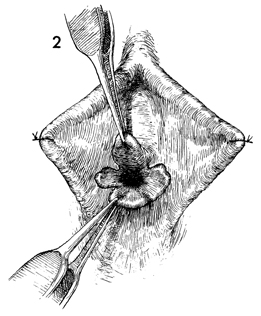
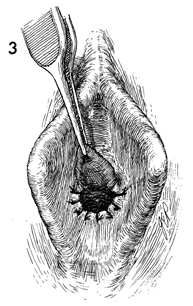
Hymenectomy Hymenectomy may be indicated in the presence of (1) an imperforate hymen creating a mucocolpos, a hematocolpos, or hematometra at menarche or (2) a perforated hymen with hymenal hypertrophy obstructing intercourse. The latter can be frightening and can be associated with major hemorrhage if the lateral pudendal artery is lacerated along with the hymen during initial attempted intercourse. Hymenectomy is performed to open the hymen without hemorrhage and to leave a patent introitus. Physiologic Changes. The procedure allows proper drainage of the vagina and permits the vaginal intercourse. Points of Caution. If a mucocolpos or hematocolpos is present, the hymen should be incised as the initial procedure, but not removed in order to allow adequate drainage and to restore normal anatomy prior to reconstruction. Caution should be observed in performing this operation in a clinic, office, or other outpatient facility where adequate resources are not available for control of hemorrhage. Technique
|
|||||
Copyright - all rights reserved / Clifford R. Wheeless,
Jr., M.D. and Marcella L. Roenneburg, M.D.
All contents of this web site are copywrite protected.