|
||||||||||||
Bartholin's Gland Cyst Marsupialization Excision of Vulvar Skin, with Split-Thickness Skin Graft Vaginal
Outlet Closure of Wide Local Excision of the Vulva Wide
Local Excision Alcohol
Injection Cortisone
Injection Excision
of the |
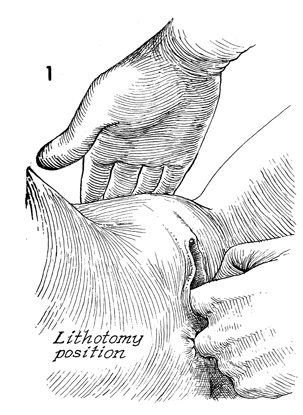
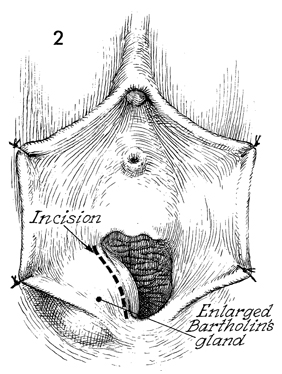
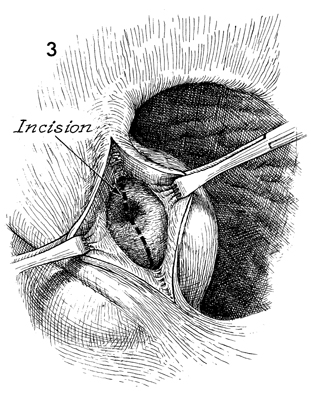
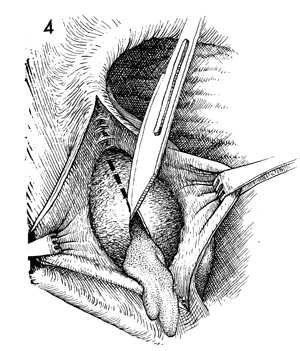
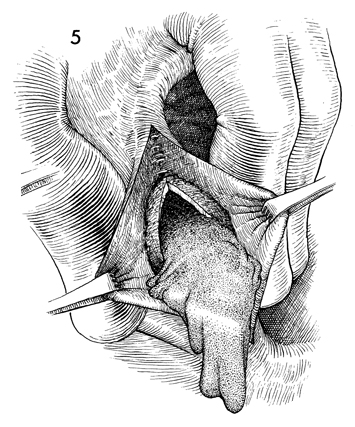
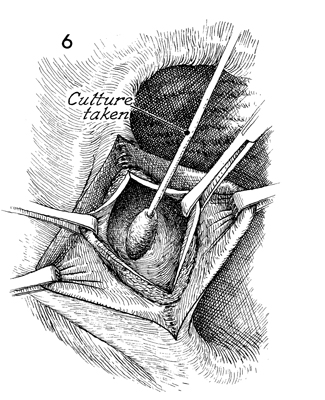
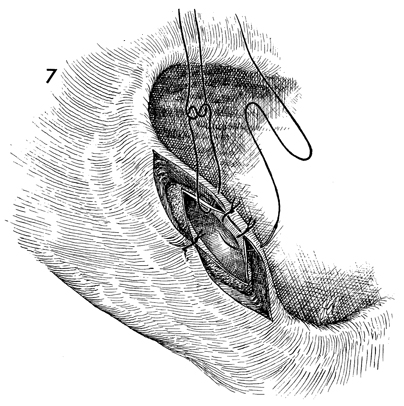
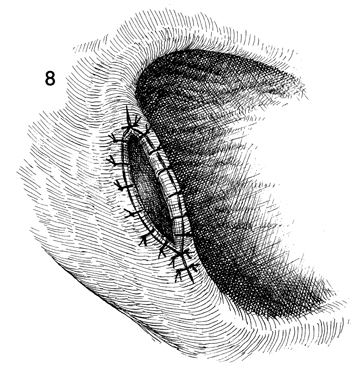
Bartholin's Gland Cyst Marsupialization Marsupialization of the Bartholin's gland is generally indicated when there is a large abscess that makes surgical excision of the gland difficult. In this operation, the surgeon opens wide the wall of the abscess and allows the purulent exudate to drain. The membrane of the abscess is then sutured to the vaginal mucosa and to the skin of the introitus in order to effect granulation and reepithelialization of the wound from the bottom of the abscess to the top. The operation is fast. Hemostasis is not difficult and can be performed under local anesthesia. The purpose of marsupialization of the Bartholin's gland is to exteriorize the abscess in such a fashion that it will become epithelialized from the base. Physiologic Changes. If marsupialization is successful, the epithelium within the gland will be epithelialized with squamous epithelium. Points of Caution. The opening into the gland must be sufficient to promote adequate drainage. Technique
|
|||||||||||
Copyright - all rights reserved / Clifford R. Wheeless,
Jr., M.D. and Marcella L. Roenneburg, M.D.
All contents of this web site are copywrite protected.