
Malignant
Disease:
Special Procedures
Staging
of Gynecologic
Oncology Patients With
Exploratory Laparotomy
Subclavian Port-A-Cath
Peritoneal Port-A-Cath
Application
of Vaginal
Cylinders for Intracavitary
Radiation Therapy
Application
of Uterine Afterloading Applicators
for Intracavitary Radiation Therapy
Pelvic High-Dose
Afterloader
Abdominal
Injection of Chromic Phosphate
( ) )
Supracolic
Total Omentectomy
Omental Pedicle "J"
Flap
Tube Gastrostomy
Total Vaginectomy
Radical
Vulvectomy
With Bilateral Inguinal
Lymph Node Dissection
Reconstruction
of the
Vulva With Gracilis Myocutaneous Flaps
Transverse
Rectus
Abdominis Myocutaneous
Flap and Vertical Rectus
Abdominis Myocutaneous
Flap
Radical
Wertheim
Hysterectomy With
Bilateral Pelvic Lymph
Node Dissection and With Extension of the Vagina
Anterior Exenteration
Posterior Exenteration
Total Pelvic
Exenteration
Colonic
"J" Pouch Rectal
Reservoir
Kock Pouch
Continent Urostomy
Omental "J" Flap
Neovagina
Ileocolic
Continent Urostomy (Miami Pouch)
Construction
of Neoanus
Gracilis Dynamic Anal
Myoplasty
Skin-Stretching
System Versus Skin Grafting
Gastric
Pelvic Flap for
Augmentation of Continent Urostomy or Neovagina
Control
of Hemorrhage in Gynecologic Surgery
Repair
of the Punctured
Vena Cava
Ligation
of a Lacerated
Internal Iliac Vein and
Suturing of a Lacerated Common Iliac Artery
Hemorrhage
Control in
Sacrospinous Ligament
Suspension of the Vagina
Presacral
Space
Hemorrhage Control
What
Not to Do in Case of Pelvic Hemorrhage
Packing
for Hemorrhage
Control
Control
of Hemorrhage
Associated With Abdominal Pregnancy |
Repair of the Punctured Vena
Cava
Technique

The surgeon is frequently
faced with small circular defects in the wall of the inferior
vena cava above the bifurcation caused by evulsion of the
perforator vein entering the para-vena cava lymph nodes.
Hemorrhage is copious and immediate. The first step in control
of this hemorrhage is to apply pressure with the finger,
the second step is to gain exposure by suctioning blood from
the abdominal cavity, extending the incision, etc., and the
third step is to obtain vascular instruments. |
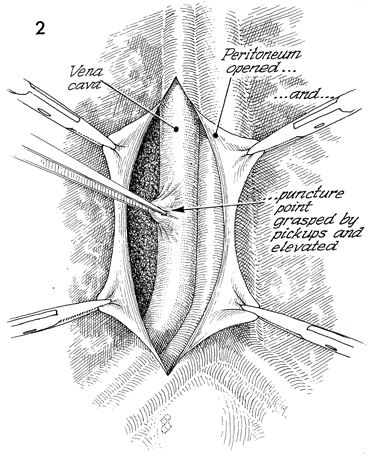
The small circular defect
in the vena cave can be grasped with smooth vascular pickups. |
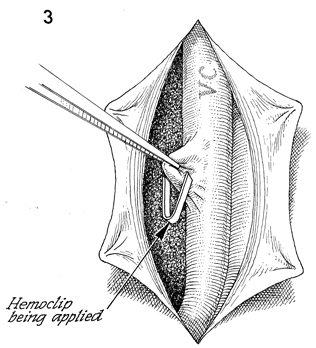
A stainless steel hemoclip
can be applied to the tented portion of the vena cava (VC).
Excess blood should be washed from the area with saline. |
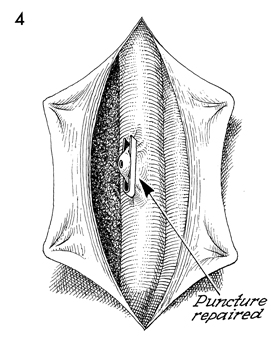
The repaired puncture should
be observed for several minutes. We have discontinued resuturing
the incised peritoneum over the vena cava. The remaining
aortic and vena cava lymphadenectomy should continue. |
|