|
||||||||||
Malignant
Disease: Staging
of Gynecologic Application
of Vaginal Application
of Uterine Afterloading Applicators Abdominal
Injection of Chromic Phosphate Radical
Vulvectomy Reconstruction
of the Transverse
Rectus Colonic
"J" Pouch Rectal Ileocolic Continent Urostomy (Miami Pouch) Construction
of Neoanus Skin-Stretching
System Versus Skin Grafting Gastric
Pelvic Flap for Control
of Hemorrhage in Gynecologic Surgery Repair
of the Punctured Ligation
of a Lacerated Hemorrhage
Control in Presacral
Space What
Not to Do in Case of Pelvic Hemorrhage |
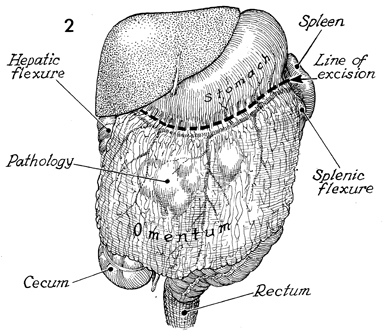
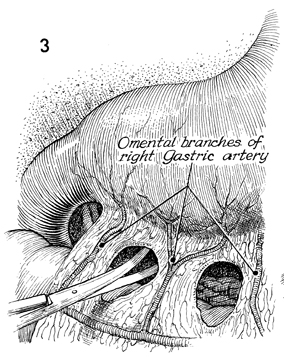
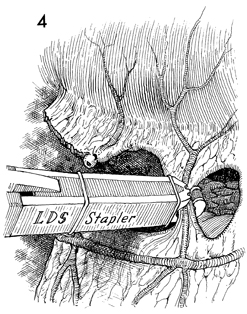
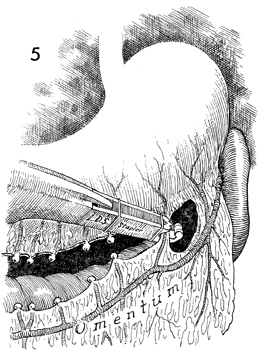
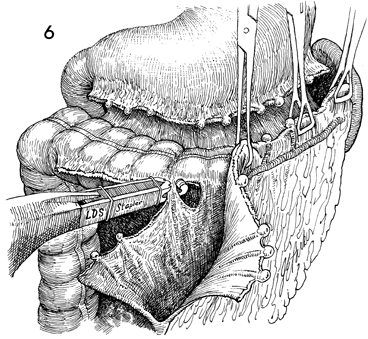
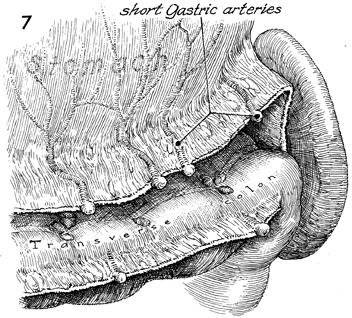
Supracolic Total Omentectomy Supracolic total omentectomy is performed in conjunction with surgery for ovarian carcinoma. It is important that patients with ovarian carcinoma be operated on through an extended midline incision, generally one from the xiphoid to the symphysis. It is difficult to perform an adequate omentectomy through a transverse or Pfannenstiel incision, and all too often such omentectomies result in incomplete excision of the tumor-bearing omentum, leaving tumor in the remaining portion of the omentum. It is instructive to discover on pathology the degree of micrometastasis in the omentum associated with ovarian carcinoma when clinically the omentum appears to be tumor free. The purpose of the operation is to remove the total omentum and all gross and microscopic metastases therein. Physiologic Changes. None. Points of Caution. The omentum should be removed from the greater curvature of the stomach and transverse colon. Care must be taken to secure the small omental branches of the right gastric artery. Meticulous hemostasis should be achieved. Technique
|
|||||||||
Copyright - all rights reserved / Clifford R. Wheeless,
Jr., M.D. and Marcella L. Roenneburg, M.D.
All contents of this web site are copywrite protected.